Progeria was first described in the nineteenth century. The mysterious disease is often thought of as premature aging.
兒童早衰癥的最早記載是在19世紀。這種神秘的疾病通常被認為是過早衰老。
Children with progeria are normal for their first year of life, but then develop medical problems normally seen in the elderly.
患有早衰癥的兒童在一歲前一切正常,但之后會患上老年人才會得的疾病。
Their bones weaken. Their skin wrinkles. They lose their hair.
他們的骨骼變得脆弱,皮膚逐漸松弛,頭發開始脫落。
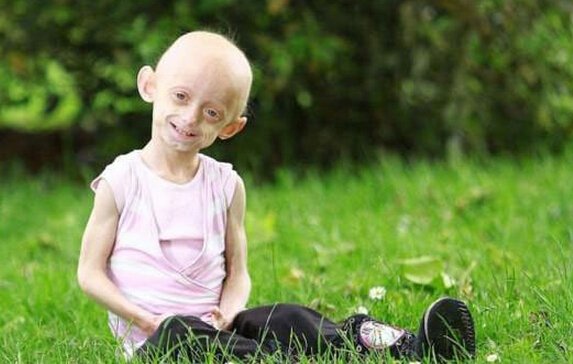
They die from heart attacks or strokes brought on by hardened arteries and high blood pressure. None lives past their early teens.
他們可能會死于由動脈硬化及高血壓引發的心臟病或中風。沒有一位患者能夠活過少年早期。
In 2003, researchers discovered what causes progeria: a genetic point mutation.
2003年,研究人員發現了少年早衰癥的病因:基因點突變。
That means that when genes are being copied to make egg or sperm, just one position in one DNA strand is copied wrong.
這是指當基因復制形成卵細胞或精子時,DNA單鏈上的某一處復制出現異常。
It is like copying a pancake recipe and replacing baking powder with salt. The pancake is not going to rise.
例如,你照著食譜做煎餅,卻錯把鹽誤認為發酵粉。煎餅當然無法發酵。
For children with progeria, the gene that encodes lamin A, a protein in the cell’s nucleus, is faulty.
對于患有早衰癥的兒童來說,其體內編碼核纖層蛋白A(細胞核內的一種蛋白質)基因是有缺陷的。












